
[ home port |
lectures |
labs |
discussion |
surf |
email guest prof. ]
Tides
Chapter
8
Tides
Tidal Characteristics
Tides are single waves
that stretch across ocean basins.
They are also shallow-water waves because their
wavelengths greatly exceed the depth of the
ocean.
They occur due to complex interactions of the moon and
sun.
Origin
of the Tides
Unlike wind-driven
surface waves, tides are cause by two principal
factors:
Gravitational
attraction
Centrifugal force
Gravitational Attraction
All masses are drawn
to each other.
The moon because of its closeness to the Earth exerts a
greater gravitational effect on the Earth than the Sun,
despite the fact that the Sun is much more massive than the
Moon.
Gravitational Effect of Moon
(Figure 8-5a)

(courtesy of NASA JPL, Topex-Poseidon
Centrifugal Forces
arise as the Earth and
Moon revolve around one another.
unequal masses of the Earth and Moon the center of
rotation lies beneath the Earth’s surface.
The water of the ocean shifts away from the center of
rotation creating a second tidal bulge.
Centrifugal Forces: Center of
Rotation
(Figure 8-5b)
2 Bulges
from Gravitational Attraction & Centrifugal
Force
(Figure 8-5c)
Origin
of the Tides
(Cont.)
The motion of water
around the basin is a rotary wave.
The crest is at one
side of the basin.
The trough is at the other side of the basin.
Tides have
characteristics of both progressive and standing
waves.
Dynamic
Model of theTides
(Figure 8-8a)
Dynamic
Model of the Tides
(Figure 8-8b)
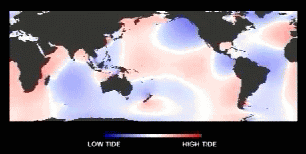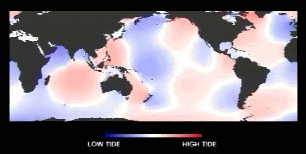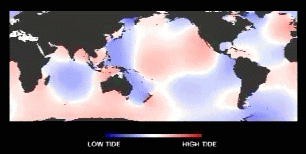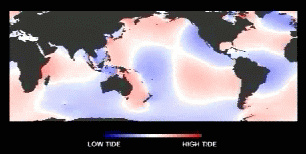
Tidal waves are rotary waves w/in an ocean basin...
(courtesy of NASA JPL, Topex-Poseidon
Key
Features of Tides
High tide : Wave
crest
Low tide : Wave trough
Tidal range : Wave height
Tidal periods depending on location:
12 hours, 25
minutes
24 hours, 30 minutes
Classification by Daily Record
Diurnal: have one high
tide and one low tide daily (high lat).
Semidiurnal: have two
high tides and two low tides daily (low lat).
Mixed: there are two
high tides and two low tides daily, but of unequal shape
(mid lat).
Classificaton by Monthly Record
Spring tide: phase
when tidal range is maximal.
Neap tide: phase when tidal range is
minimal.
There are 2 spring and 2 neap tides each
month
Spring
& Neap Tides
Spring tides occur
when the Earth, Sun, and Moon are aligned.
New Moon and Full Moon
phases
Constructive interference
Neap tides occur when
the Sun and Moon are aligned at right angles to one
another.
Quarter Moon
phases
Destructive interference
Sun/Moon/Earth - Spring & Neap
(Figure 8-7a)
Tidal
Periods
The reason why tidal
periods are not exactly 24 hours or 12 hours in length is
that the Moon moves forward in it’s orbit each day.
In fact it takes 50 additional minutes for a spot on the
Earth’s surface to regain it’s position relative
to the Moon.
The equilibrium model of the tides is good, but it does
not give us a detailed and accurate description of the
tides in the real world, where the oceans are separated by
continents and not infinitely deep.
Marine
Biorhythms
Cyclical behaviors
associated with tidal rhythms.
The diurnal activity
of fiddler crabs.
The spawning behavior of the grunion fish.
Diurnal
Activity of Fiddler Crabs
(Figure B8-4)
Summary
Tides are long
shallow-water waves generated by the gravitational
attraction of the Moon and the Sun on the ocean’s
water.
Scientists develop models to explain tidal
patterns.
Electrical power can be generated by having flood and
ebb tide currents flow over specially designed
turbines.
[ home port |
lectures |
labs |
discussion |
surf |
email guest prof. ]
http://dusk.geo.orst.edu/oceans/tides.html



